Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a geographic area where plants, animals, and other organisms, as well as weather and landscape, work together to form a bubble of life.
An ecosystem is a community of living and non-living things that work together.
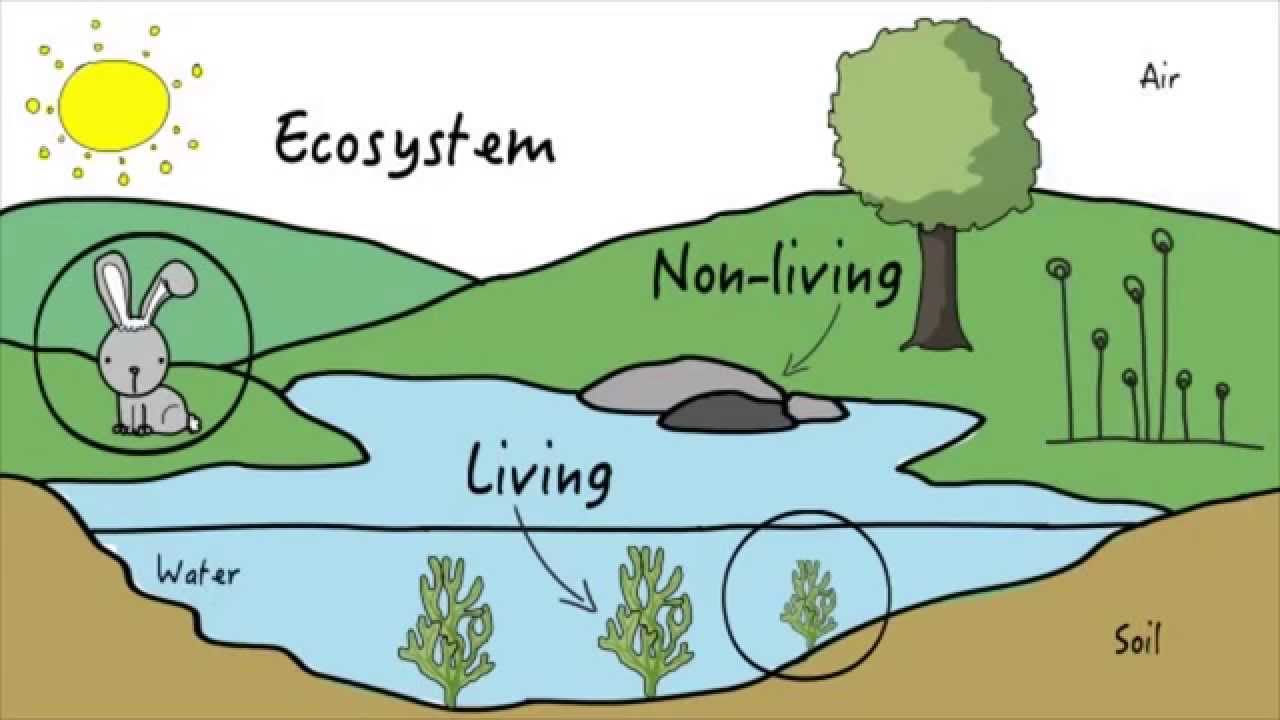
An ecosystem is a system consisting of biotic and abiotic components that function together as a unit. The biotic components include all the living things (like Human beings, Plants, Insects, Mammals, Animals, Reptiles, Bacteria etc.) whereas the abiotic components are the non-living things (like rocks, sand, glass, sun, water, weather, climate, natural events etc.).
Factors affecting Ecosystem
- Deforestation and Soil erosion: Deforestation is the clearance of a forest or removal of trees where the land is converted to a non-forest use, such as agriculture and construction of houses, industries, dam etc. It may also lead to extinction of plant and animal species.
Soil erosion is the displacement of the upper layer of soil. The loss of trees, which anchor the soil with their roots, causes soil erosion. - Mining practices: Mining is the process of extracting the valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth. The minerals or ores are then refined to extract the valuable elements, such as metals, gems, minerals, etc. Some of the environmental impacts of mining include erosion, loss of biodiversity and contamination of soil, groundwater and surface water by chemicals from the mining processes.
- Pollution: Pollution is the process of making land, water, air or other parts of the environment dirty and not safe or suitable to use. Pollution is caused by pollutants, which may be solid, liquid or gaseous in nature. Pollution is the effect of undesirable changes in our surroundings that have harmful effects on plants, animals and human beings. For example, factories consume a lot of water and electricity and release harmful chemicals in air, land and water, thus contaminating the atmosphere.
- Overexploitation: Continued overexploitation can lead to resource depletion and put a number of threatened and endangered resources at risk of extinction. The example of Overexploitation are Overfishing, overhunting, overharvesting etc. For example:- In the case of fish and marine invertebrates, Overfishing depletes some species to very low numbers and drives others to extinction.
- Faulty utilisation of water resources: India is still suffering from flood and droughts due to faulty utilisation of water resources. Dams have displaced crores of tribal people, drowned million hectares of rich forest areas, failed to prevent and control floods etc.