Turing Test in Artificial Intelligence
In 1950, Alan Turing introduced a test to check whether a machine can think like a human or not, this test is known as the Turing Test. In this test, Turing proposed that the computer can be said to be an intelligent if it can mimic human response under specific conditions.
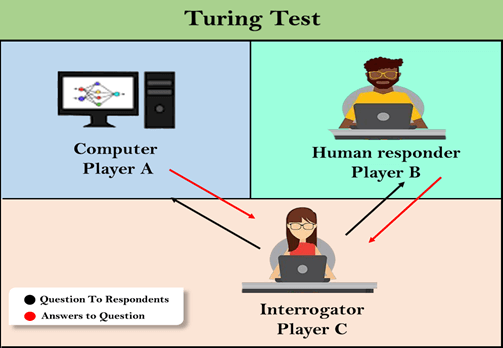
The Turing test is based on a game. This game involves three players in which one player is a Computer, another player is human responder, and the third player is a human Interrogator, who is isolated from other two players and his job is to find that which player is machine among two of them.
Consider, Player A is a computer, Player B is human, and Player C is an interrogator. Interrogator is aware that one of them is machine, but he needs to identify this on the basis of questions and their responses.
The conversation between all players is via keyboard and screen so the result would not depend on the machine's ability to convert words as speech.
The test result does not depend on each correct answer, but only how closely its responses like a human answer. The computer is permitted to do everything possible to force a wrong identification by the interrogator.
The questions and answers can be like:
Interrogator: Are you a computer?
PlayerA (Computer): No
Interrogator: Multiply two large numbers such as (256896489*456725896)
Player A: Long pause and give the wrong answer.
In this game, if an interrogator would not be able to identify which is a machine and which is human, then the computer passes the test successfully, and the machine is said to be intelligent and can think like a human.
Some examples that attempt the Turing Test are ELIZA, Parry, Eugene Goostman etc.
Features required for a machine to pass the Turing test:
- Natural language processing: NLP is required to communicate with Interrogator in general human language like English.
- Knowledge representation: To store and retrieve information during the test.
- Automated reasoning: To use the previously stored information for answering the questions.
- Machine learning: To adapt new changes and can detect generalized patterns.
- Vision (For total Turing test): To recognize the interrogator actions and other objects during a test.
- Motor Control (For total Turing test): To act upon objects if requested.