Basics of Data Literacy
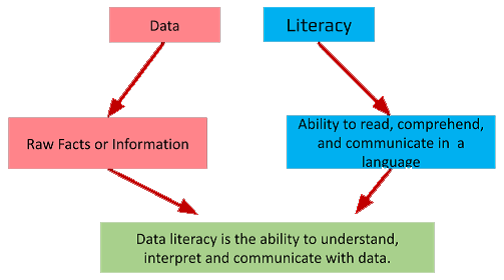
Data Literacy: Data literacy means knowing how to understand, work with, and talks about data. It's about being able to collect, analyse, and show data in ways that make sense. It refers to the ability to read, understand, interpret, and communicate with data effectively.
Data Pyramid explains the different stages of working with data-
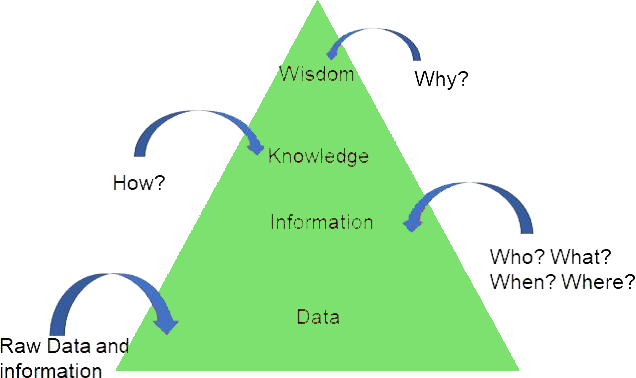
- Data is available in a raw form which is not very useful.
- Data is processed to extract the information about the world.
- Information about the world leads to knowledge of how things are happening.
- Wisdom (Intelligence) allows us to understand why things are happening in a particular way.
Impact/Importance of Data Literacy
- Better Decision-Making: Data-literate individuals can make decisions based on facts instead of assumptions or guesses.
- Improved Communication: It enhances the ability to convey complex information clearly to different audiences.
- Increased Innovation: With data literacy, we can work with new and better ideas, products, or ways of doing things
- Solve Complex problems: It makes easier to break the complex problems into sub-problems, identify the trands and solve it effectively.
Data Security

Data security is the practice of protecting digital information from unauthorized access, corruption, or theft throughout its entire lifecycle. It involves protecting computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from harmful attacks.
Why Data Security is important?
Due to the rising amount of data in the cloud there is an increased risk of cyber threats (Cyber-attacks). It is necessary to control and protect the transfer of sensitive or personal information.
Data Privacy
Data privacy refers to the practice of protecting personal information from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. It involves ensuring that individual's private data is handled responsibly, securely, and in compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Best Practices for Data Privacy:
- Understanding what data you have collected, how it is handled, and where it is stored.
- Necessary data required for a project should only be collected.
- User consent while data collection must be of utmost importance.
Cyber Security
Cyber Security means protecting computers, networks, and data from attacks by hackers, viruses, or other threats.
Best Practices for Cyber Security:
Do‘s
- Use strong, unique passwords with a mix of characters for each account.
- Activate Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for added security.
- Download software from trusted sources and scan files before opening.
- Prefer websites with "https://" for secure logins.
- Keep your browser, Operating System and antivirus updated regularly.
- Adjust social media privacy settings for limited visibility to close contacts.
- Always lock your screen when away.
- Connect only with trusted individuals online.
- Use secure Wi-Fi networks.
- Report online bullying to a trusted adult immediately.
Don’t ‘s
- Avoid sharing personal info like real name or phone number.
- Don't send pictures to strangers or post them on social media.
- Don't open emails or attachments from unknown sources.
- Ignore suspicious requests for personal info like bank account details.
- Keep passwords and security questions private.
- Don't copy copyrighted software without permission.
- Avoid cyberbullying or using offensive language online.