Types of Data
Data comes in many forms for the purpose of analysing and decision making. Primary types of data is discussed below:
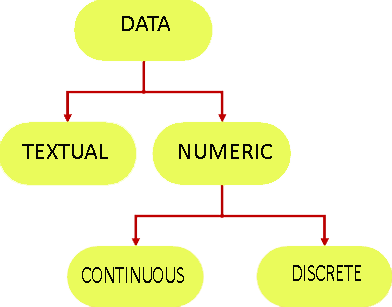
Textual Data (Qualitative Data): It provides the insights (characteristics, attributes, qualities, etc.) in the form of words or phrases. It may be subjective and descriptive.
For example- Customer feedbacks (comments, reviews, opinions), Social media sentiments, etc.
Numeric Data (Quantitative Data): It provides the information of something in the form of numerical values. It can be countable and measurable.
For example- Sales data, Meter reading, scores, surveys etc.
Qualitative Data vs Quantitative Data
| Qualitative Data (Textual) | Quantitative Data (Numeric) |
|---|---|
| It describes qualities or characteristics. | It represents quantities or numeric values. |
| It is collected through observations, interviews, open-ended questions, etc. | It is collected through structured data collection methods like surveys, sensors, etc. |
| It provides in-depth insights. | It provides precise, measurable and testable data. |
| It answers "Why" and "How" types of questions. | It answers "How many" and "How much" types of questions. |
| It may comes in the form of text, audio, video, images, etc. | It may comes in the form of numbers, percentages, frequencies, etc. |
| It can be used for Natural Language Processing (NLP) models. | It is used for Statistical Data / Data Science models. |
| Examples: Customer reviews, Case studies, Opinions, preferences, experiences/td> | Examples: Test marks, Ratings, Sensor readings, Cricket Score, Restaurant Bills, etc. |
Numeric Data is further classified as:
Continuous data: Continuous data represents numbers that are measurable and can take any value within a range, including fractions and decimals. For example- height, weight, temperature, voltage, etc.
Discrete data: Discrete data is a numeric data that contains only whole numbers and cannot be fractional. For example- The number of students in the class – it can only be a whole number, not in decimals.
Types of Data used in three domains of AI:
Data Science: Numeric Data in tabular form (Excel sheet, tables etc.)
Computer Vision: Visual Data (Images or videos)
NLP: Textual Data (Documents, PDF files, etc.)